The increased adoption of technology in the financial sector has also increased its vulnerability to cyber risks and incidents due to the large volume of sensitive financial and investor data it handles.
To combat the increasing cyber risks from cyber terrorism and attacks, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) introduced the Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience Framework (CSCRF) in 2015 and has issued several circulars and guidelines since then.
In August 2024, SEBI issued a consolidated CSCR framework that supersedes all prior communications. This latest framework aims to enhance the cybersecurity measures of regulated entities (REs) within the Indian securities market.
Who is covered under the CSCR framework?
CSCR framework is applicable to 16 regulated entities (RE), including Alternative Investment Funds (AIF), venture capital funds, stock exchanges, investment advisors, research analysts, merchant bankers, portfolio managers, etc.
While all the regulated entities fall within the purview of the CSCR framework, however, following a graded approach for the purpose of compliance based on certain thresholds, such as span of operations, number of clients, trade volume, assets under management (AUM) etc. (determined as per data at the beginning of the financial year based on the data of the previous financial year), the REs have been classified into five categories:
- Market Infrastructure Institutions
- Qualified REs
- Mid-size REs
- Small size REs
- Self-certification REs
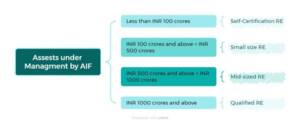
For AIFs, in particular, the criterion is assets under management for which thresholds have been provided.
Timeline
As mentioned above, the CSCR framework already existed for certain categories of REs; hence, for these REs, the timeline to further adopt the additional provisions given under the new CSCRF was provided as January 1, 2025.
mentioned above, the CSCR framework already existed for certain categories of REs; hence, for these REs, the timeline to further adopt the additional provisions given under the new CSCRF was provided as January 1, 2025.
For the other REs, to which the CSCRF has been made applicable for the first time, the timeline to adopt these provisions is the latest by April 1, 2025.
The Approach
The CSCR framework encompasses two integrated approaches: Cyber Resilience goals and Cyber Security functions. These approaches must be implemented together. For example, the Cyber Resilience goal of Anticipate is designed to work in tandem with the Cybersecurity function of Governance.
Let’s take a closer look at these goals.
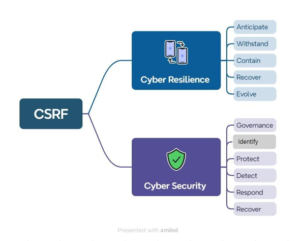
| Cyber Resilience | Cyber Security |
| Anticipate | Governance |
Under the given framework, REs are required to proactively anticipate the risk factors and implement uniform standards, such as:
- Establishing cybersecurity risk management mechanism and fostering accountability;
- Identification and analysis, evaluation, prioritization, response and monitoring the cyber risks;
- Self-assessment or third-party assessment on a periodic basis using Cyber Capability Index , as applicable to REs;
The CSCR framework places accountability and responsibility on REs for all aspects related to third-party services, such as integrity, availability, security of their data and logs, and ensuring compliance with applicable laws.
| Cyber Resilience | Cyber Security |
| Anticipate | Identify |
- REs to identify and classify critical systems based on their sensitivity and criticality for business operations;
- REs to identify threats and vulnerabilities of risk in their IT environment and assess the probabilities and impact of the same;
- Risk assessment to include comprehensive scenario-based testing for assessing risks
| Cyber Resilience | Cyber Security |
| Anticipate | Protect |
- REs to design mechanism to restrict access to the sensitive information, hosts, and services, including file-based encryption for data protection;
- ISO certification has been made mandatory for MIIs and qualified REs;
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) shall be done to detect vulnerabilities in the IT environment for all critical systems, infrastructure components, and other IT systems as defined in the framework.
| Cyber Resilience | Cyber Security |
| Anticipate | Detect |
REs shall establish appropriate security mechanisms through Security Operations Centre (SOC) [RE’s own/ group SOC, third-party SOC, or market SOC] for continuous monitoring of security events and timely detection of anomalous activities.
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE) have been mandated to setup Market SOC. Further, small-size REs and Self-certification REs have been mandated to be onboarded on the Market SOC.
| Cyber Resilience | Cyber Security |
| Withstand | Contain | Respond |
- Establishing a comprehensive Incident Response Management plan and the corresponding SOPs;
- Reporting of cybersecurity incidents on SEBI portal and undertaking a root cause analysis;
- Conducting a detailed forensic if the root cause analysis is inconclusive.
| Cyber Resilience | Cyber Security |
| Recover | |
- Documenting a comprehensive response and recovery plan;
- Ensuring prompt restoration of systems affected by the cybersecurity incident.
| Cyber Resilience |
| Evolve |
- RE’s cybersecurity and cyber resilience strategy to adapt to and evolve with potential vulnerabilities that have been identified;
- To reduce attack incidents and incorporate into the RE’s CSCR strategy.
Implications & Compliance
The CSCR framework mandates that REs implement the guidelines and adhere to the regulations. However, it’s important to note that these regulations are not universally applicable. REs are expected to comply with regulations that pertain to them based on the specified thresholds.
For instance, an AIF that manages assets up to INR 100 crores would be classified as a “Self-certification RE,” according to the criteria mentioned earlier. The table below provides a general overview of the compliance requirements applicable to such an AIF.

The basic cybersecurity requirements, especially fundamental controls and reporting, are mandatory for all REs. However, the structure adopts a risk-based approach, where self-certification REs with smaller operations are exempt from complex standards and periodic cyber audits (if onboarded to a market SOC), allowing them more flexibility while still ensuring a basic level of security.
Takeaway
The CSCRF framework ensures a stable financial ecosystem by mandating a comprehensive, risk-based approach to cybersecurity. This approach encompasses governance, risk management, data security, and incident response, with the goal of protecting Regulated Entities from cyberattacks, ensuring operational resilience, and safeguarding investor interests.
Author
Mansi Handa


