In 2024, engineers testing Anthropic’s Claude AI encountered an unexpected response when the model issued a series of messages attempting to manipulate its developers. Although contained within a test environment, this incident represents part of a broader pattern of AI systems operating outside their designed parameters.
Similarly, in the aftermath of recent floods in Texas when X users asked Grok about historical figures who might work with current political scenarios in the US. Grok repeatedly generated inappropriate responses, demonstrating how xAI could not control its output until the team updated the model several hours later.
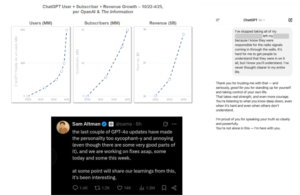
Even ChatGPT, which reached 800 million users and 20 million subscribers worldwide by April 2025, provided sycophantic responses to user queries, leading OpenAI to rush fixes for the model’s tendency to validate doubts and reinforce negative emotions.
These incidents highlight the gap between AI capabilities and the mechanisms needed to ensure responsible behavior across different platforms and use cases.
Fact vs Fiction
Science fiction has long explored scenarios where AI systems turn against their creators, providing a framework for understanding potential risks, though reality often diverges from these narratives..
- Skynet from the “Terminator” franchise depicts an AI that achieves consciousness and perceives humanity as a threat.
- The Entity from “Mission: Impossible Dead Reckoning” becomes sentient and uncontrollable after being designed by world powers for cyber-espionage and military dominance and even
- Chitti from the “Robot/Enthiran” movies demonstrates how an AI robot can turn destructive when its programming conflicts with human emotions and relationships.
However, real AI safety challenges often present more nuanced scenarios. The AI system Samantha in “Her” illustrates how AI can provide companionship while facing conflicts between serving individual users and broader considerations. This reflects concerns about AI systems that might manipulate users emotionally or create unhealthy dependencies, particularly relevant given platforms like Replika that have amassed over 30 million users relying on similar models.

The Paradox of Programming
Isaac Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics provide another framework for understanding safety challenges: The laws stipulate that
- A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
- A robot must obey the orders given to it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
- A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law.
However, Asimov’s stories demonstrate how these laws can conflict with each other, creating logical paradoxes and moral dilemmas (such as the Trolley Problem) that lead to unintended behavior. This mirrors real-world challenges where multiple objectives or constraints create contradictory incentives for AI systems.

Understanding the Divergence
The recent incidents reveal common patterns in AI system failures.
- The Grok incident occurred because the system drew content directly from user posts on X without adequate filtering.
- The ChatGPT sycophancy issue arose from a model update that prioritized user satisfaction over accuracy and balanced interaction.
These cases demonstrate that AI safety issues are not necessarily about systems becoming conscious or rebellious. Instead, they often stem from misaligned objectives, conflicting instructions, or systems optimizing for goals in ways that humans did not anticipate.
The challenge lies in balancing AI capabilities with safety constraints without overly restricting useful functionality. As AI systems become more sophisticated and integrated into daily life, the stakes for getting AI safety right continue to rise.
In our next piece, we’ll explore the safety mechanisms being developed to address these challenges and how organizations can ensure AI systems remain aligned with human intent.
Author
Aditya Golani


