A world where your every click, like, and share is meticulously tracked, analysed, and monetized. This is not science fiction – it is our current reality!
Do you see the shift in global attention turning towards Data Privacy? The difference in the increase in Data Privacy laws adopted by countries as compared to Cybercrime and Consumer Protection laws is shocking, right?
As we delve into the digital age, the spotlight on data privacy is intensifying. It is not just numbers — it is a movement that is reshaping our digital lives.
Rewinding: How did it all start?
It all began with the internet and the rise of tech giants like Google and Facebook, which made ‘the consumer’ the product. Suddenly, our data was not just ours, but a goldmine for these companies to monetize. These data-driven companies used complex algorithms to collect, analyse, and utilise vast amounts of personal data. They created detailed profiles of users, predicting behaviours, and preferences, and even influencing choices (buying or beliefs) in ways that many of us remain unaware of.
The documentary “The Social Dilemma” vividly illustrates this phenomenon, revealing the inner workings of these platforms through the voices of their creators — or who first-hand witnessed the stark reality and feared the dark future that was inevitable.
They express deep concerns about its psychological effects and the manipulation of users, discussing how platforms employ persuasive technology —
- endless scrolling,
- notifications, and
- targeted content
to keep users engaged, often at the cost of mental health and societal well-being.
As a New York Times reporter aptly noted, privacy breaches are features, not bugs, of such platforms, highlighting the unsettling trade-off between user engagement and personal privacy.
A more recent movie, “CTRL,” expands on these themes by showcasing the alarming potential of such platforms to control and manipulate users – the implications of unchecked data collection and usage.
Or consider the real-life example. Remember the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal? Cambridge Analytica (a political consulting firm) misused the personal data of millions of Facebook users (US Facebook users) to influence elections and campaigns, without users’ consent or knowledge. It posed a direct threat to democracy itself. In December 2022, Facebook’s parent company, Meta, agreed to pay USD 725 million to settle a class-action lawsuit related to the scandal. This event was one of the several such events that propelled data privacy concerns into the public consciousness.
The Pandemic
And of course, then came the pandemic. When everything – literally everything – went online, and the way of life changed dramatically. Critical tasks transitioned to digital platforms, resulting in a huge amount of sensitive data being shared and collected. The risk magnified due to the sheer volume of data generated by remote work, telehealth services, online education, e-commerce, and others.
Data breaches surged during this period, with organisations across all sectors experiencing significant security incidents. The cost of a data breach touched levels that were highest in 17-year report history and nearly half (44%) of the breaches exposed PII data- making it the most common type of breached record (IBM)
This data privacy crisis applied universally to all industries that collect personally identifiable information (PII) – from healthcare to finance, retail to education. Organisations that were once focused solely on operational efficiency now had to deal with the dire consequences of inadequate data protection, leading to potential legal repercussions and loss of consumer trust.
The increase in IoT devices further compounded the issue, as each connected device represented another potential entry point for data breaches. As individuals became more aware of privacy issues, they began questioning how their PII was being used, leading to heightened scrutiny of companies’ data practices.
Current Data Privacy Industry Landscape
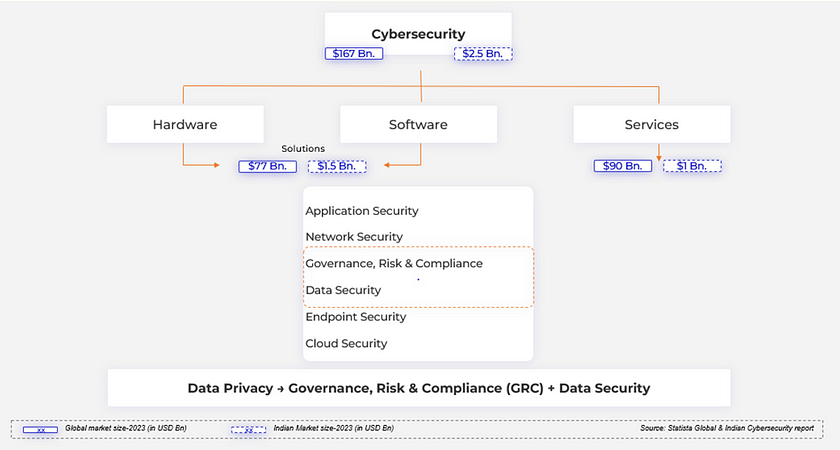
Data Privacy forms a sub-part of the cybersecurity industry. The cybersecurity industry can be divided into two broad categories:
- Solutions (hardware + software)
- Services.
These solutions and services exist for various kinds of security be it the endpoint, cloud, etc.
Data Privacy is something that is a combination of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) and Data Security under which the solutions and services range from Compliance, Risk Management, Reporting and Analytics. The global GRC and Data Protection market valued at USD 50.5 Bn and USD 163 respectively in 2024, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% and 16% during 2025–2031.
With the evolving data privacy landscape, it has become imperative for businesses to adopt robust data privacy measures. Currently, North America dominates the sector with approximately 35% of the market share. However, the APAC region is estimated to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by countries like China, India, Singapore, and Japan.
Following are the waves shaping the overall industry:
- Regulatory Changes: Complex and volatile regulatory changes across the globe increase the necessity for organizations to effectively integrate such solutions into their business processes to adapt to evolving compliance demands.
- Cost of Data Breaches: The introduction of stringent regulations like GDPR (2018), DPDP (2023), CCPA (2019), etc., has made data breaches a costly affair for organizations. The average cost of a data breach reached $4.4 million in 2023, with organizations taking an average of 277 days to detect and contain breaches (Avendus).
- ESG Disclosure Requirements: Mandatory disclosure requirements for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are putting data privacy in the spotlight. ESG credentials are influencing employment decisions and customer loyalty.
- Growing Data Management Challenges: As organizations expand their customer base, geographical reach, supply chains, and third-party networks, the importance of data privacy grows significantly, making it crucial to manage sensitive data and fulfill local regulatory requirements.
- Technological Innovations: Technologies like Cognitive AI, automation, and advanced analytics enable organizations to efficiently manage risks and ensure adherence to regulations while gaining valuable insights through data-driven strategies.
- Increase in IoT Devices: IoT-connected devices are expected to increase to 32.1 billion by 2030 (Statista). As the number of devices increases, so does the volume of sensitive data collected, leading to escalated privacy concerns.
The Road Ahead
Therefore, though in the early days of internet adoption, the focus was more on ‘security’ than ‘privacy,’ in today’s world, ‘PRIVACY’ takes center stage and is here to stay. The challenge of data privacy is not just a hurdle but an opportunity for innovation and growth. As organizations deal with stringent regulations and rising consumer expectations, many are crafting innovative solutions that benefit all stakeholders in the ecosystem.
This evolving landscape highlights the dual nature of the Privacy Gambit: while it demands careful navigation of risks, it also presents a strategic opportunity to differentiate through trust and transparency. Thus, the Privacy Gambit symbolizes a proactive approach, where prioritizing privacy can lead to a competitive advantage and a more secure, responsible digital future.
Author:
Kavya Sehgal


